Plastic Concrete Footing Forms Calculator - Metric
This calculator estimates the total volume of concrete required when using plastic footing forms and a cylindrical concrete tube on top, using metric units. Results are provided in cubic metres (m³), cubic feet (ft³), and cubic yards (yd³).
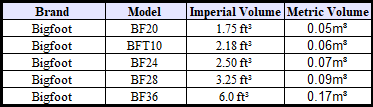

Calculator Inputs
- Capacity of Plastic Form (m³) - Predefined volume of one plastic form.
- Diameter of Concrete Tube (mm) - Width across the concrete tube form.
- Height of Concrete Tube (m) - Vertical height of the cylindrical concrete portion.
- Number of Plastic Forms (#) - How many complete plastic + tube assemblies are needed?

Need imperial values? Use the Footing Formwork Calculator.
Other useful shape calculators:
Plastic Concrete Footing Forms Calculator - Metric
Calculator
- enter the plastic form capacity in cubic metres
- the tube diameter in millimetres
- the tube height in metres (for multiple forms, add all individual height sections together)
- enter the number of forms being used
Results
- required concrete in cubic metres
- amount of concrete needed in cubic feet
- concrete needed in cubic yards
This tool helps estimate the volume of concrete required when combining prefabricated plastic forms with cast-in-place cylindrical tube forms using metric dimensions. Always round up slightly to allow for overfill and spillage.
Formulas Used
Let:
\[ C_f = \text{Capacity of plastic form (in ml)} \\ D = \text{Tube diameter (mm)} \\ H = \text{Tube height (m)} \\ N = \text{Number of forms} \]Convert diameter to radius in metres:
\[ r = \frac{D}{2000} \]Volume of cylindrical tube (ml):
\[ V_{\text{tube}} = \pi \cdot r^2 \cdot H \]Total volume per form (ml):
\[ V_{\text{one}} = C_f + V_{\text{tube}} \]Total volume for all forms (ml):
\[ V_{\text{total}} = V_{\text{one}} \cdot N \]Unit Conversions:
\[ V_{\text{ftl}} = \frac{V_{\text{total}}}{0.0283168466} \quad,\quad V_{\text{ydl}} = \frac{V_{\text{ftl}}}{27} \]Example Calculation
Given:
\( C_f = 0.12 \, \text{m}^3,\; D = 300 \, \text{mm},\; H = 0.8 \, \text{m},\; N = 4 \)
- \( r = 300 / 2000 = 0.15 \, \text{m} \)
- \( V_{\text{tube}} = \pi \cdot (0.15)^2 \cdot 0.8 \approx 0.0565 \, \text{m}^3 \)
- \( V_{\text{one}} = 0.12 + 0.0565 = 0.1765 \, \text{m}^3 \)
- \( V_{\text{total}} = 0.1765 \cdot 4 = 0.706 \, \text{m}^3 \)
- \( V_{\text{ftl}} \approx \frac{0.706}{0.0283168466} \approx 24.94 \, \text{ft}^3 \)
- \( V_{\text{ydl}} \approx \frac{24.94}{27} \approx 0.92 \, \text{yd}^3 \)